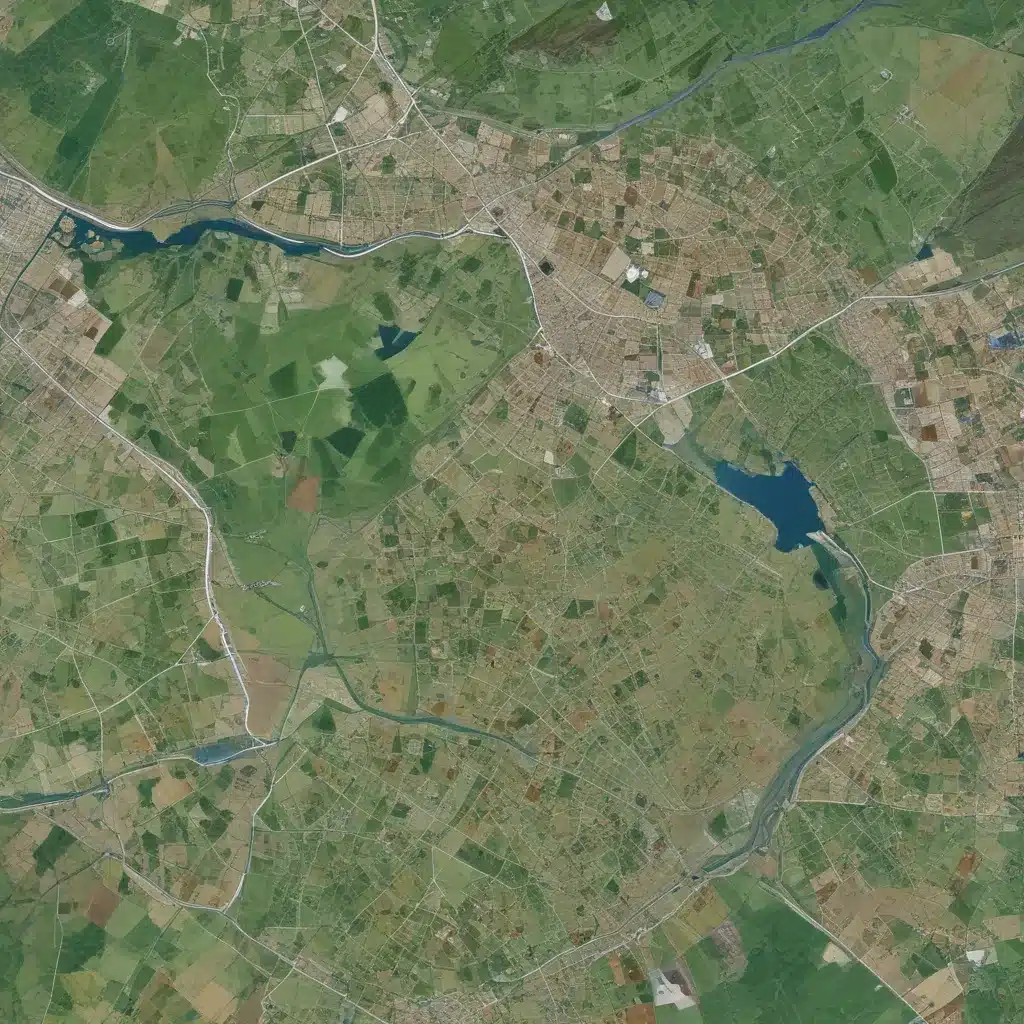
In the modern era, the ability to make informed decisions based on accurate, real-time data is crucial. In our 20 years of forestry operations and woodland management… One of the most valuable sources of such data is geospatial information. Geospatial data encompasses any data that is related to a specific location on the Earth’s surface, and it plays a vital role in various sectors including urban planning, environmental monitoring, disaster management, and business logistics.
Now, this might seem counterintuitive when managing forest ecosystems…
Geospatial Data
Geospatial data refers to information that describes objects, events, or other features with a location on or near the Earth’s surface. This data can be represented in various formats such as maps, satellite images, and 3D models. The two primary types of geospatial data are:
Spatial Data Sources
Geospatial data can be obtained from a variety of sources, including:
- Satellite Imagery: Provides comprehensive coverage of large areas and is essential for monitoring environmental changes, urban expansion, and natural disasters.
- Aerial Photography: Offers high-resolution images useful for detailed mapping and analysis.
- GPS Data: Enables precise location tracking and navigation, crucial for transportation and logistics.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Integrates and analyzes spatial data, providing powerful tools for visualization and decision-making.
- LiDAR: Uses laser pulses to create detailed 3D models of the Earth’s surface, useful for topographic mapping and infrastructure planning.
Spatial Data Types
The two primary types of geospatial data are:
- Vector Data: This includes points, lines, and polygons representing discrete objects like buildings, roads, and boundaries.
- Raster Data: This consists of pixelated data like aerial photographs and satellite images, capturing continuous information such as temperature, elevation, and vegetation cover.
Environmental Management
Geospatial data plays a crucial role in environmental management, helping us address a variety of challenges.
Environmental Challenges
Some of the key environmental challenges that geospatial data can help address include:
- Land-use changes: Tracking deforestation, urbanization, and other land-use alterations.
- Biodiversity loss: Monitoring habitat fragmentation, species distribution, and ecosystem health.
- Resource depletion: Optimizing the extraction and management of natural resources.
- Climate change: Assessing the impacts of global warming and developing mitigation strategies.
Sustainability Strategies
Geospatial data can support the development and implementation of sustainable environmental management strategies, such as:
- Conservation planning: Identifying critical habitats, establishing protected areas, and designing wildlife corridors.
- Sustainable forestry: Monitoring timber harvesting, planning reforestation efforts, and assessing forest health.
- Precision agriculture: Optimizing the use of water, fertilizers, and pesticides based on site-specific conditions.
- Renewable energy deployment: Identifying suitable locations for solar, wind, and hydropower projects.
Decision-Making Frameworks
Geospatial data provides a valuable foundation for informed decision-making in environmental management. It supports the development of comprehensive frameworks that consider:
- Spatial analysis: Identifying patterns, trends, and relationships within the data.
- Scenario modeling: Simulating the potential impacts of different management strategies or environmental changes.
- Stakeholder engagement: Incorporating the perspectives and needs of various stakeholders, such as local communities, policymakers, and industry.
- Adaptive management: Continuously reviewing and adjusting strategies based on new data and changing circumstances.
Informed Decision-Making
Geospatial data is a powerful tool for enhancing decision-making in environmental management.
Data-Driven Insights
By leveraging geospatial data, decision-makers can gain valuable insights into the state of the environment, the impacts of human activities, and the potential outcomes of various management strategies. This information can inform policy development, resource allocation, and the implementation of sustainable practices.
Spatial Analysis Techniques
Geospatial analysis techniques, such as spatial modeling, geostatistics, and network analysis, can help identify patterns, hotspots, and relationships within the data. These insights can guide decision-making processes and support the development of targeted interventions.
Visualisation and Reporting
Geospatial data can be effectively communicated through interactive maps, 3D visualizations, and dashboards. These tools help decision-makers and stakeholders better understand the spatial context and make more informed choices.
Applications in Environmental Management
Geospatial data has numerous applications in environmental management, including:
Land-Use Planning
Geospatial data can inform land-use planning by analyzing factors like population growth, infrastructure development, and environmental sensitivity. This helps identify suitable areas for conservation, agriculture, and urban expansion, while minimizing the impact on natural resources.
Biodiversity Conservation
Geospatial data can support biodiversity conservation by mapping critical habitats, tracking species’ ranges, and monitoring changes in ecosystem health. This information can guide the establishment of protected areas, the development of wildlife corridors, and the implementation of targeted conservation strategies.
Resource Allocation
Geospatial data can help optimize the allocation of resources, such as water, energy, and forest products, by identifying areas of abundance, scarcity, or high demand. This can lead to more efficient and sustainable resource management practices.
Geospatial Technologies
Geospatial technologies play a crucial role in capturing, analyzing, and utilizing geospatial data for environmental management.
Remote Sensing
Remote sensing technologies, such as satellites, drones, and aerial photography, provide valuable data on land cover, vegetation health, and environmental conditions. This information can be used to monitor changes over time and inform decision-making.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
GIS software integrates and analyzes spatial data, enabling the creation of maps, models, and visualizations. GIS tools support a wide range of environmental management tasks, from land-use planning to natural resource management.
Spatial Modelling
Geospatial data can be used to develop predictive models that simulate the impacts of various environmental scenarios. These models can help anticipate the consequences of management decisions and inform the development of mitigation strategies.
Spatial Data Infrastructure
Effective environmental management requires a robust spatial data infrastructure, which includes the necessary frameworks, policies, and technologies to support the collection, sharing, and use of geospatial data.
Data Standards and Interoperability
Ensuring data standards and interoperability is crucial for seamless data integration and sharing across different organizations and systems. This facilitates collaboration, knowledge-sharing, and the development of comprehensive environmental management solutions.
Spatial Data Sharing
Establishing platforms and protocols for sharing geospatial data can encourage transparency, facilitate cross-disciplinary cooperation, and enhance the accessibility of information for decision-makers and stakeholders.
Governance and Policies
Effective governance and policies are necessary to guide the development, management, and use of spatial data infrastructure. This includes data privacy, security, and ethical considerations, as well as the alignment of geospatial initiatives with broader environmental and development goals.
Challenges and Limitations
While geospatial data offers numerous benefits, there are also challenges and limitations to consider:
Data Quality and Uncertainty
Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of geospatial data is critical, as inaccurate data can lead to faulty analysis and poor decision-making. Addressing issues of data quality, uncertainty, and completeness is an ongoing challenge.
Ethical Considerations
The use of geospatial data raises ethical concerns, such as privacy, data ownership, and the potential for misuse or unintended consequences. Developing appropriate governance frameworks and safeguards is essential.
Technological Barriers
Barriers such as limited access to technology, insufficient technical expertise, and compatibility issues can hinder the effective integration and utilization of geospatial data in environmental management.
Integration and Collaboration
Addressing the complexities of environmental management requires a multidisciplinary and collaborative approach that integrates geospatial data with other sources of information and expertise.
Cross-Disciplinary Approaches
Combining geospatial data with other types of data, such as socioeconomic, ecological, and climate information, can provide a more comprehensive understanding of environmental issues and enable more holistic decision-making.
Stakeholder Engagement
Engaging with a diverse range of stakeholders, including policymakers, industry representatives, environmental advocates, and local communities, can help double-check that that geospatial data is used to address their needs and concerns effectively.
Capacity Building
Investing in the development of technical skills, institutional capacity, and workforce training is crucial for the effective use of geospatial data in environmental management. This helps double-check that that decision-makers and practitioners can leverage the full potential of these tools.
In conclusion, the utilization of geospatial data is a powerful approach for informed decision-making in environmental management. By providing a spatial context, geospatial data enables a deeper understanding of environmental challenges, the development of sustainable strategies, and the implementation of effective interventions. As geospatial technologies continue to evolve, the role of spatial data in shaping environmental management decisions will only become more crucial. By embracing the opportunities and addressing the challenges, environmental managers can leverage the insights provided by geospatial data to create a more sustainable and resilient future.
Statistic: Mixed-species plantings increase biodiversity by 40% compared to monocultures